In the quest for environmentally friendly energy options, the world has seen a notable shift towards renewable sources, with solar energy leading the way, especially in heating systems. The growing concerns about climate change and environmental sustainability make comparing solar energy with traditional fossil fuels like oil and gas increasingly important.
The changes in how the U.S. gets its energy over the last thirty years play a crucial role. Back in 1991, a whopping 88% of U.S. electricity came from fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and petroleum. Nuclear energy contributed 8%, with only 4% coming from renewable sources.
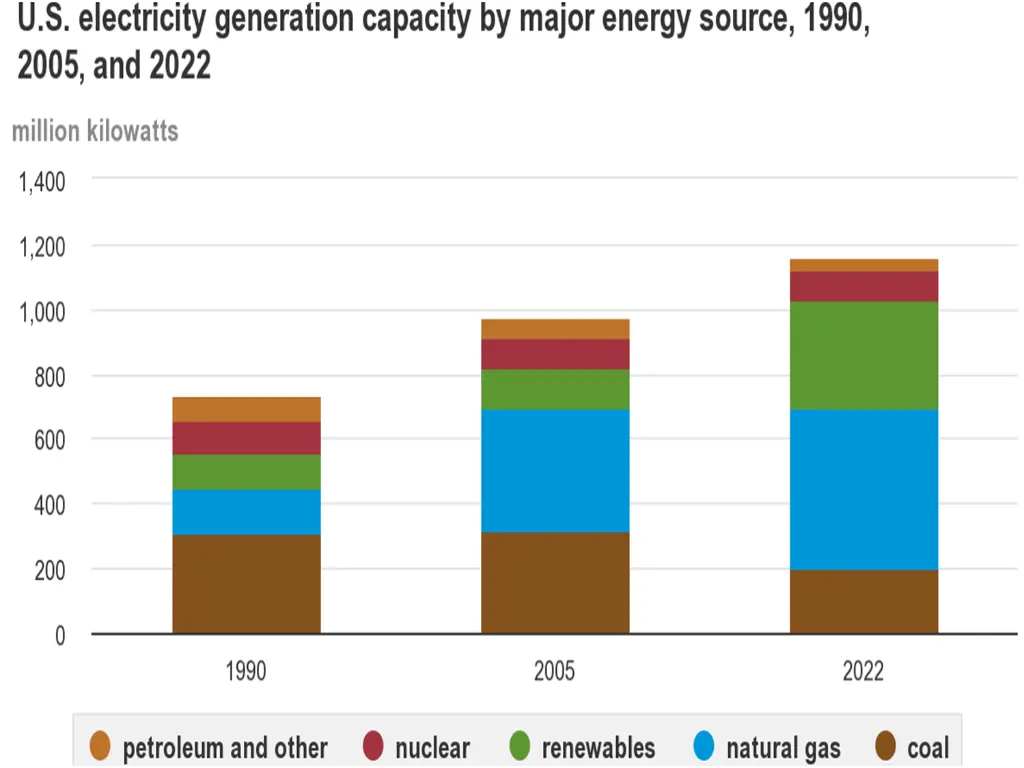
Source: eia.gov
Fast forward to 2022, and the narrative has drastically changed. Fossil fuel reliance has dropped to 60%, while renewable energy sources have risen significantly to 22%. Nuclear energy maintains an 18% share, highlighting a significant shift in the nation’s energy consumption patterns.
However, this shift is not uniform across states, as different energy landscapes have emerged based on geography, economics, and policies. Some states have fully embraced renewable energy, harnessing solar power for heating from the ample sunlight, while others, tied to traditional fossil fuel reserves, continue to rely on oil and gas.

Beyond the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy provides an attractive alternative for heating applications, significantly reducing dependence on finite fossil fuel resources. We’ll closely examine solar heating house systems, exploring their efficiency, economic feasibility, and environmental impact in contrast to traditional oil and gas-based heating systems. Our goal is to give a clear picture of the factors in each region that affect whether people choose to use solar heating systems for homes.SPS-2-02 Banner
Source: buildinggreen
Source: bradpettitt
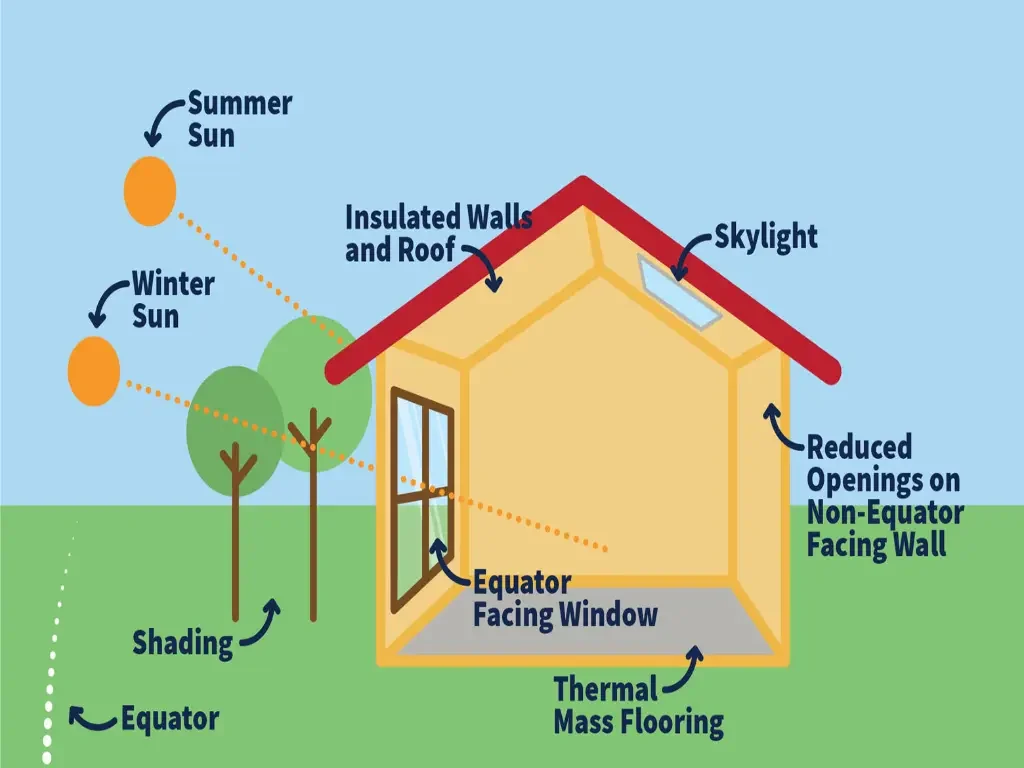
For a passive solar heating system to work effectively, your house needs the right orientation, unlike active solar home heating.
Source:powerhug
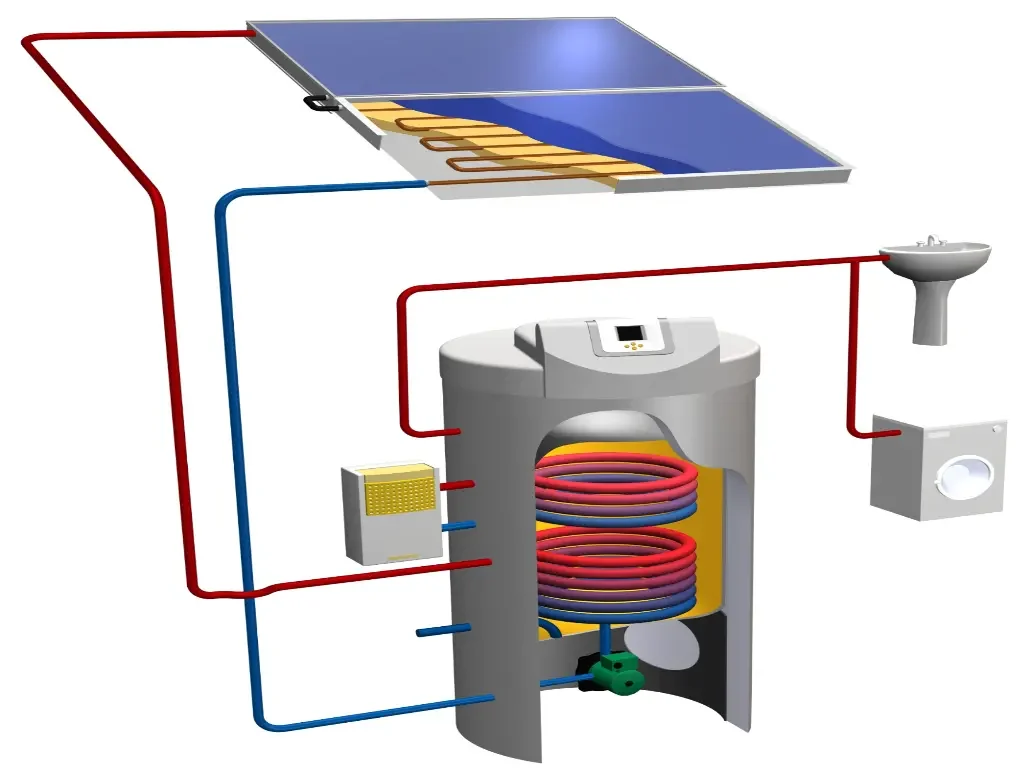
In a typical pressurized polypropylene glycol solar line setup, the immersed coil helps transfer solar heat into the hot water storage tank through the indirect immersed coil. In this arrangement, the tank is filled with water and indirectly heated by the hot glycol from the evacuated tube solar collector outlet. This design is commonly used in colder climates and works well for retrofits with an electric or natural gas domestic water heater. In these situations, the solar hot water storage tank preheats domestic cold water before entering the water heater.
Solar heat can be transferred to the hydronic floor heating circuits via the storage tank for rooms heated with hydronic floor heating. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a storage tank with two inlets and outlets:
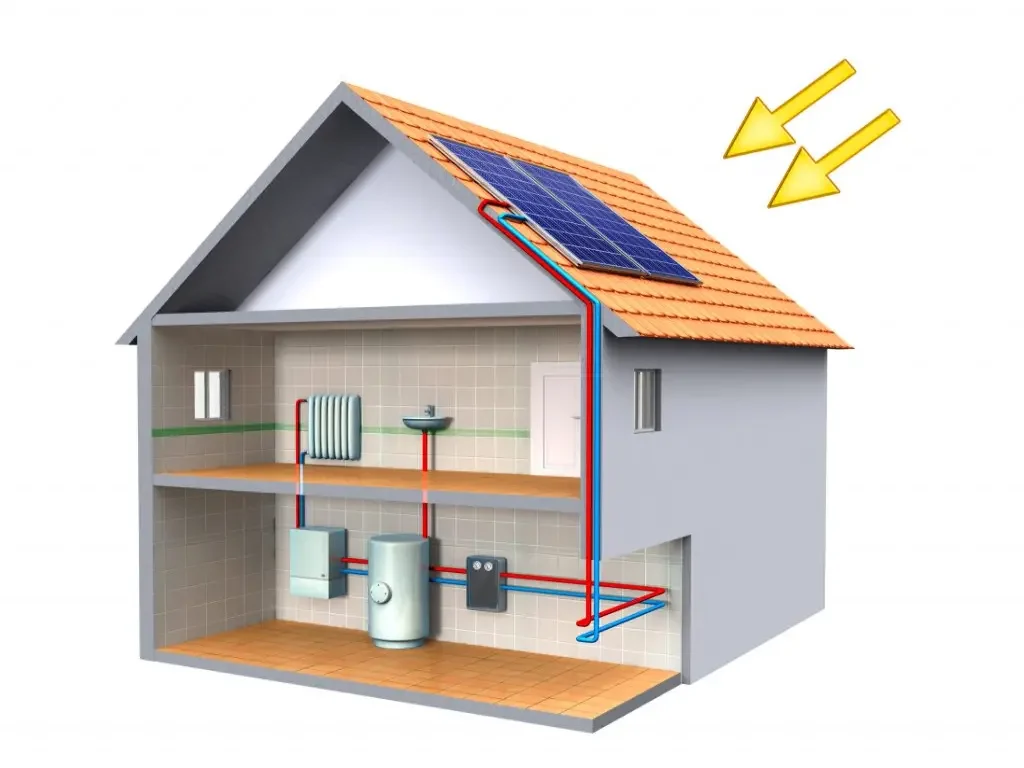
Source: electricrate
Navigating solar home heating costs involves meticulously examining regional variations, energy-efficient options, and upfront installation expenses. Homeowners are presented with an opportunity to strike a balance between long-term savings and immediate costs, making informed decisions that align with both their financial goals and environmental considerations. Understanding these economic considerations becomes paramount in ensuring a warm and cost-effective home environment as the winter season unfolds.

Source: businessreport
While oil and gas systems provide a more consistent energy supply and boast higher efficiency rates, the environmental harm associated with fossil fuels raises concerns. The choice between solar and traditional systems ultimately depends on carefully considering specific needs, environmental priorities, and geographical context. As technology advances, the reliability of solar heating systems is expected to improve further, making them increasingly competitive alternatives in the quest for sustainable heating solutions.

Source: dfwsolarelectric
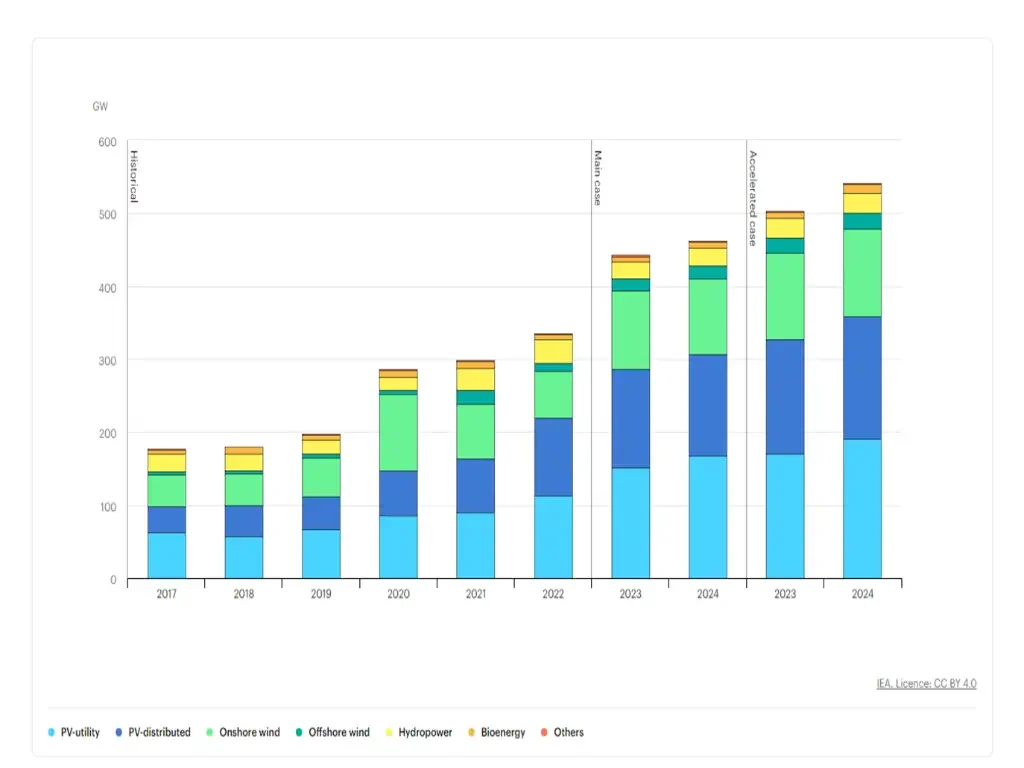
Source: iea
This growth trajectory is poised to continue into the next year, with the world’s total renewable electricity capacity reaching an impressive 4,500 gigawatts (GW).


How much is your electricity bill per month?
Help us understand what you`re currently spending
Beyond the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy provides an attractive alternative for heating applications, significantly reducing dependence on finite fossil fuel resources. We’ll closely examine solar heating house systems, exploring their efficiency, economic feasibility, and environmental impact in contrast to traditional oil and gas-based heating systems. Our goal is to give a clear picture of the factors in each region that affect whether people choose to use solar heating systems for homes.
Solar Heating System
Solar heating for homes is a way of using sunlight to warm up water or air inside buildings. Instead of turning the sun’s energy into electricity, as solar panels do, solar-powered heating captures the sun’s heat directly. This system is eco-friendly and renewable, collecting energy from the sun to create warmth.
What Is Passive Solar Heating?
There are two common solar-powered heating methods: passive and active. Passive solar space heating occurs when sunlight enters a building through its windows, warming the interior. Designs that maximize solar heating house systems typically include south-facing windows (in the northern hemisphere). These windows allow the sun to illuminate solar heat-absorbing walls or floors inside the building. The building materials absorb solar energy, heating the interior through natural radiation and convection. During the summer, window overhangs or shades prevent excessive sunlight, helping to keep the building cool.
What Is Active Solar Heating?
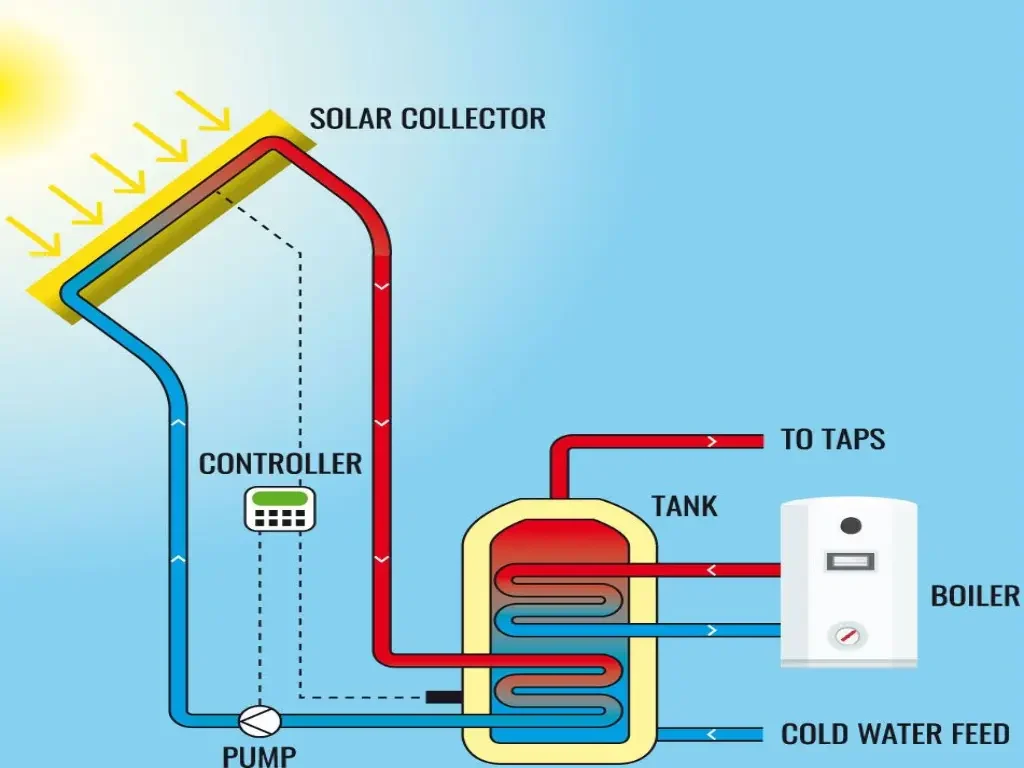
The active solar heating system is widely used to harness solar energy in homes. It involves collecting, storing, and utilizing solar heat, primarily heating water and spaces. “Active” refers to using pumps and fans to transfer the captured heat for storage or immediate use.How Home Solar Heating Systems Work
Solar thermal panels of all types act as heat exchangers.- First, tube solar collectors with 15, 20, 25, and 30 tubes, which are outside, absorb solar energy and transfer it to a liquid.
- This fluid, whether water, a mixture of polypropylene glycol and water, or another type, circulates in a closed loop, heating another secondary fluid suitable for the specific application – water for domestic hot water or hydronic air handling units.

- the lower coil collects the solar energy collected by the solar collectors
- the upper coil transfers the solar energy to the hydronic heating circuits
- the main inlet and outlet of the tank can be used to heat domestic hot water.
Economic Considerations: Navigating the Costs of Solar Heating
As the winter chill approaches, homeowners across the United States are confronted with the perennial challenge of balancing comfort with rising energy costs. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average cost of electricity in the U.S. stands at 15.47 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). For the winter of 2022-2023, estimates for electric heating costs for U.S. homeowners average $1,359, marking a 10% increase from the previous winter. Delving into regional nuances, electric heating costs will range from $1,400 to $1,700 in most regions, with the South experiencing relatively lower costs at approximately $1,250. These figures underscore the economic considerations that influence household energy expenses. When evaluating heating systems, the annual cost chart provides valuable insights: Geothermal Heat Pump: $1,681 Ductless Heat Pump: $2,297 Ducted Heat Pump: $2,871 Electric Baseboard: $6,202 The data suggests a wide range of costs associated with different heating systems, emphasizing the need for homeowners to make informed decisions based on their unique circumstances. It highlights the significant energy-saving potential of electric heat pumps compared to traditional electric resistance heating methods like furnaces and baseboard heaters. Ducted air-source heat pumps, the most common type, can reduce energy consumption by approximately 50%. More advanced alternatives, such as geothermal heat pumps, offer an even greater reduction of up to 60%. While these upgrades result in monthly savings, it is crucial to factor in the sizable upfront installation costs associated with these energy-efficient systems. It’s important to note that geothermal heat pumps, although highly efficient, may not be feasible for all homeowners due to the requirement of digging large trenches near or under the home. This highlights the importance of considering both the economic and practical aspects when choosing a heating system.
Efficiency and Reliability
When it comes to heating our homes, the efficiency and reliability of the chosen system are crucial factors. In this chapter, we explore the capabilities of home solar heating systems, evaluating their effectiveness in various climates across the USA. We also scrutinize the impact of regional weather patterns on the performance of solar home heating and weigh the reliability of traditional oil and gas systems in different environmental conditions within the USA.Understanding the Efficiency of Solar Heating Systems
Solar heating systems, leveraging the power of sunlight, play a role in energy-conscious heating solutions. The efficiency of these systems varies across the diverse climates of the USA. Solar energy heating operates efficiently in states blessed with abundant sunshine, like Arizona or California, offering high performance. However, the efficiency may fluctuate in regions experiencing frequent cloud cover or colder climates, such as the Pacific Northwest or the Northeast.- Solar Energy Factor (SEF)
Impact of Regional Weather Patterns
The United States exhibits a broad range of climates, from the arid Southwest to the snowy Northeast. These diverse regional weather patterns exert a substantial influence on the performance of home solar heating systems. In states blessed with abundant sunshine, these systems consistently operate at peak efficiency. However, areas characterized by unpredictable weather may encounter fluctuations in system performance. It is imperative to recognize the impact of climate change on the entire energy system. As temperatures rise, there is a notable shift in the demand for heating and cooling across the nation. Furthermore, these temperature increases affect the efficiency of crucial components such as PV panels, thermo-electric power plants, and transmission lines. The changing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events can result in technology downtime, posing challenges to the reliability of the energy supply. These physical effects influence supply reliability, cost dynamics, and local environmental considerations. Some of these impacts may prompt an augmented reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to increased greenhouse gas emissions.Reliability of Solar vs Natural Gas and Oil Systems
Exploring the efficiency and reliability equation requires examining traditional oil and gas heating systems prevalent across the USA first. These systems demonstrate reliability in various environmental conditions, providing consistent warmth. Whether facing the chill of a Northern winter or the heat of a Southern summer, oil and gas systems remain dependable. However, their reliance on finite fossil fuels prompts questions about long-term sustainability and environmental impact, urging a careful evaluation of trade-offs. Let’s look into the reliability of solar heating systems vs oil and gas systems, examining key factors that influence their dependability.- Consistency of Energy Supply
- Efficiency Comparison

Technological Advancements in Solar Heating
In the realm of solar heating, individual states are driving innovation to harness the maximum potential of renewable energy sources.- One notable advancement is the integration of smart inverters and sensors, allowing for more precise control and optimization of solar heating systems.
- States like California and Massachusetts lead in adopting these innovations, utilizing smart grids and temperature gauges to enhance the efficiency of solar heating installations. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and adjustment, ensuring optimal performance based on local weather conditions and energy demand.
- Advancements in solar collector design and materials increase efficiency and reliability. Innovations in collector design, such as improved heat-absorbing coatings and selective surfaces, enable systems to capture and convert sunlight more effectively, even in variable weather conditions. This establishes solar heating as an efficient and practical choice for various geographical and climatic scenarios.

- State-specific challenges are met with tailored solutions, emphasizing the adaptability of solar heating and cooling technology. For instance, states prone to extreme weather events, like Texas and Louisiana, have seen the development of resilient solar heating systems with enhanced durability and resistance to adverse conditions. These robust systems ensure continuous operation, even in challenging environments, contributing to the overall reliability of solar heating and cooling.
- Integrating energy storage solutions is another significant technological stride, addressing the intermittent nature of solar energy. States like Arizona and Nevada are exploring advanced energy storage technologies, including improved battery systems, to store excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours. This stored energy can then be utilized during periods of low sunlight, providing a consistent and reliable heating source. State-specific innovations, ranging from smart technologies to resilient designs, are overcoming challenges and enhancing the competitiveness of solar heating systems.
Understanding Environmental Impact
In our search for cleaner energy, we closely examine how different heating systems impact the environment. Across the country, regions have developed unique energy strategies influenced by their location, economy, and regulations. States heavily relying on oil and gas for heating tend to have a higher environmental impact due to increased emissions. Meanwhile, areas embracing electric heating with solar panels are making progress in reducing reliance on fossil fuels, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions. This emphasizes the importance of local conditions in determining the environmental impact of solar panel heating systems. Certain states are taking a stand by implementing strict environmental regulations. These regions are increasingly adopting solar heating systems to comply with regulations and create a cleaner energy future. Solar heating aligns with these goals, offering a green alternative that meets high environmental standards. Solar energy vs natural gas options reveal a significant difference in their environmental impact.Natural Gas Heating
Regular heating methods contribute to greenhouse gases responsible for climate change. Fossil fuel combustion for energy accounts for 73% of total greenhouse gas emissions. While not classified as a renewable source, natural gas is a more environmentally friendly option. It emits 30% less CO2 than oil and a substantial 45% less CO2 than coal. This lower carbon footprint contributes to the overall reliability of natural gas systems.Electric Heating With Solar Panels
As per the International Renewable Energy Agency (IREA), solar thermal energy has the potential to meet 6% of the global heat demand by 2030, leading to a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Experts indicate that the lifetime emissions from solar energy are about 48 grams of carbon per kWh, making it one of the top environmentally friendly energy sources as it is renewable.Challenges and Opportunities for Solar Heating Systems
As the world grapples with escalating energy demands the quest for sustainable alternatives has never been more critical.Energy Challenges in Industry
Industries currently account for around 35% of the world’s total energy consumption, which is expected to rise as industrial activities expand. This increased reliance on fossil fuels, our primary energy source, poses a threat due to the dwindling availability of these resources and the negative impact on the environment.Renewables in Power Generation
Efforts to create a low-carbon power system focus on swapping traditional fossil fuel power plants for renewable sources. In the United States, there has been an impressive four-fold increase in renewable energy generation within the electric power sector from 2010 to 2019, from 414 GW to about 1,650 GW. This uptick is fueled by higher fossil fuel prices and concerns about energy security, driving a robust deployment of solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind power. As depicted in the graph, solar PV capacity, encompassing both large utility-scale and small distributed systems, contributes significantly, accounting for two-thirds of this year’s anticipated increase in global renewable capacity.


