In a constantly changing world where power reliability is uncertain, it is now an absolute necessity to have a backup power system. Backup generators and batteries are two prevalent alternatives for residential backup power. Each presents distinct benefits and distinctions that necessitate householders’ consideration.
Statistics show that 54% of Americans have experienced a power outage in their homes for 12 hours or more. There is a growing trend towards the implementation of battery backup systems for residential use, with a particular emphasis on solar battery backups. These systems store grid or solar panel-generated electricity, thereby offering a continuous and silent home backup power supply in the event of blackouts. The capability of a home battery backup, such as the Tesla Powerwall, to store 13.5 kWh is sufficient to power a residence for one day.
Backup generators have historically served as the primary fallback power source for residential purposes. The North American portable generators market exceeded USD 4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow 4% from 2023 to 2032. The optimal backup generator for a home reserve power has a rated output between 5kW and 50kW. Frequently powered by petroleum, propane, or natural gas, these apparatuses transform mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Whether you are contemplating the use of a conventional backup generator or a solar backup generator for a home backup power source, it is vital that you comprehend their operation, benefits, and applications. By providing a comprehensive comparison of these two alternatives, this article intends to assist you in making an informed choice.
How Backup Generator and Battery Function?
As residential electricity consumption continues to rise, there is a corresponding surge in demand for dependable emergency power solutions as fallback power sources for the household; home battery backup and backup generators are two common alternatives. We will describe the operation of these two backup power suppliers and which one may be more suitable for your requirements in this section.
How Backup Battery Work
- In the event of a primary power outage, home battery backup systems, such as a solar backup batteries, store energy for subsequent use. Energy from the utility or renewable sources, such as solar panels, can be stored in them.
- On the primary grid, the battery backup system initiates operation automatically. This uninterrupted operation guarantees that your appliances and devices will continue to operate seamlessly.
- The energy that is retained in the backup battery is transformed into an electrical current (AC) that can be utilized by the electrical system of your residence. Whether and for how long a battery can deliver power is dependent on its capacity.
- Following the restoration of the main power, the home backup battery initiates the process of recharging in anticipation of the subsequent power outage.
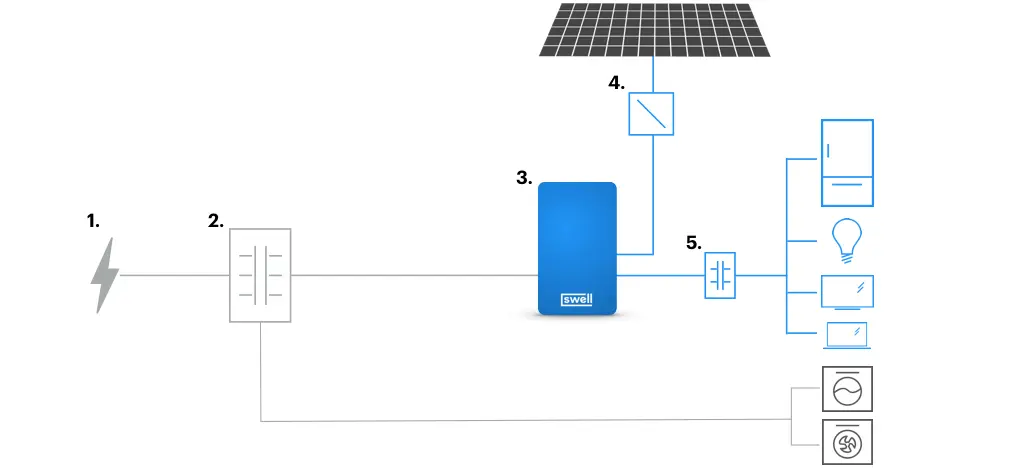
Source: Swell Energy
Backup batteries offer immediate, discreet power and are environmentally favorable, particularly when used in conjunction with renewable energy sources such as solar panels. However, due to their limited capacity, they might not be capable of supplying power to an entire residence for prolonged durations.
How Backup Generators Work
Typical fuel sources for residential backup generators include natural gas, propane, or diesel. In your region, the cost and availability of these substances will determine which backup generator is ideal for domestic backup power.
- Similar to backup batteries, the majority of contemporary generators are capable of autonomously detecting a power outage and initiating operation in order to supply supplementary power.
- The fuel is burned by the backup generator’s engine to generate mechanical energy, which is subsequently transformed into electrical energy. This energy is used to fuel the electrical system in your residence.
- The backup generator can sustain power generation in the absence of a fuel supply. Consequently, they are well-suited for extended periods of power outage.
- Upon the restoration of the main power, the backup generator closes down automatically.
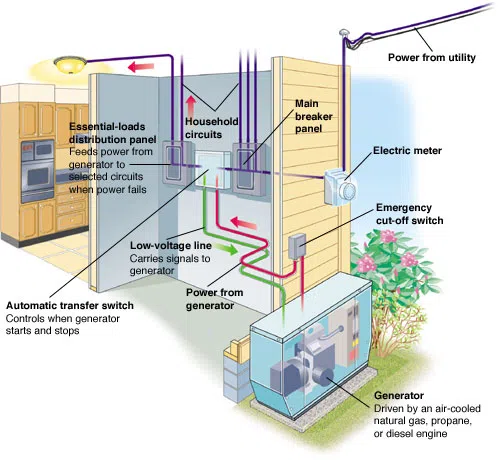
Source: This Old House
Unlike backup batteries, backup generators can supply power to a greater perimeter of a dwelling and for extended durations. Nonetheless, they generate emissions and noise and necessitate a consistent fuel supply.
As reserve power sources for the household, backup batteries, and generators each possess their own set of advantages. A home battery backup might be adequate in the event of brief, sporadic power disruptions. Consider utilizing a fuel-powered backup generator or a solar backup generator for home backup in the event of extended blackouts or for residences with high power demands. Always keep in mind your particular requirements, financial constraints, and regional conditions when selecting a secondary power solution.
Types of Backup Batteries and Backup Generators
Based on your requirements and circumstances, a backup battery or generator has its pros and cons. Knowing their different kinds will help you choose the finest backup power option for your house.
Backup Battery Types
Home backup power from batteries is efficient and eco-friendly. They provide quiet, emission-free electricity by storing and releasing energy. Two primary varieties of backup battery for home power outages are:
- Lead acid batteries. These are the most common alternatives for home backup power. Affordable and dependable, they have a shorter lifetime than other varieties and need frequent maintenance. A lifespan of 5 to 10 years is typical for these batteries.
- Lithium-ion batteries. Made of lithium-ion, these backup batteries are more costly than lead-acid but last longer, have more energy, and need less maintenance. They are employed in solar backup generators owing to their efficiency and longevity. The projected lifespan is 15 to 20 years.
Types of Backup Generator
Generators turn natural gas, propane, or diesel into electricity. They offer dependable backup power for home and come in a variety of sizes and capacities to fulfill energy demands.
Portable generators. These generators are popular emergency power sources due to their affordability and ease of installation. They must be operated manually and refueled. The power of a portable generator ranges from 3000 to 6500 watts.

Source: The Home Depot
- Standby generators. Permanent standby generators activate automatically when electricity is lost. Backup generators with greater power than portable backup generators cost extra. A home standby backup generator may hold anywhere between 6,000 and 150,000 watts of electricity.

Source: The Home Depot
- Solar backup generators. During power disruptions, solar backup generators store energy produced by solar panels in a backup battery. These eco-friendly devices can generate electricity continuously as long as there is sunshine, but they may not be enough for bigger households or prolonged poor weather.
Budget, energy demands, and personal preferences determine whether you use a home backup battery or a backup generator for backup power. You may choose better by knowing the kinds.
Alternative Power Backup Battery and Generator: Pros and Cons
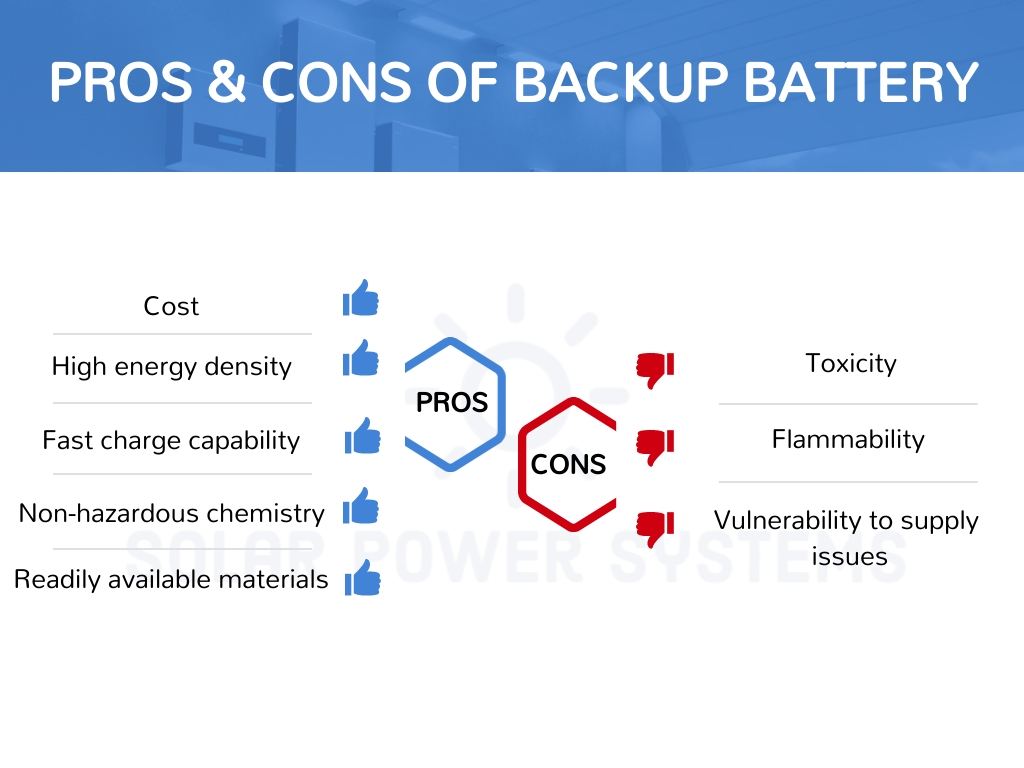
Environmental benevolence, silent operation, and reduced maintenance are all advantages of a backup power supply for the home. But they are more expensive initially and have a reduced power capacity.
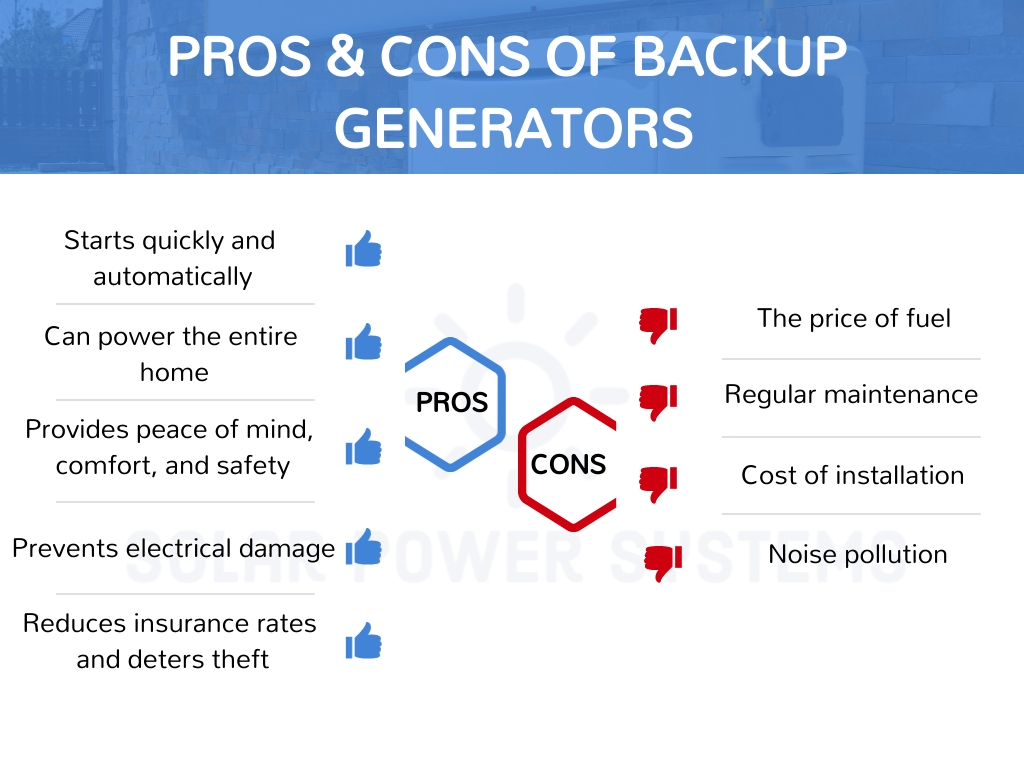
Reliable backup power for the household is provided by backup generators, which effortlessly operate large appliances. In addition, they are economical over time. Conversely, they emit carbon dioxide, are raucous, and demand routine maintenance.
Thus, your budget and particular requirements will dictate which backup power supply you select. Remember that a dependable battery reserve in the event of a backup power disruption is essential for ensuring a continuous power supply during unforeseen outages.
Backup Battery vs Backup Generator Cost
The Price of a Backup Battery
It is essential, when calculating the cost of a home battery backup for a residential power disruption, to consider everything from the initial purchase price. Wallet power backup for home can cost anywhere between $3,000 and $15,000, contingent upon factors such as power capacity and brand.
Consistent home battery backup replacement and maintenance are required for reserve battery systems. Over time, this recurring expense may substantially augment the overall cost of ownership. However, the advantages of utilizing a backup battery for residential purposes are indisputable. It is very important to pay attention to capacity, as the price of the solar backup battery changes depending on the capacity.
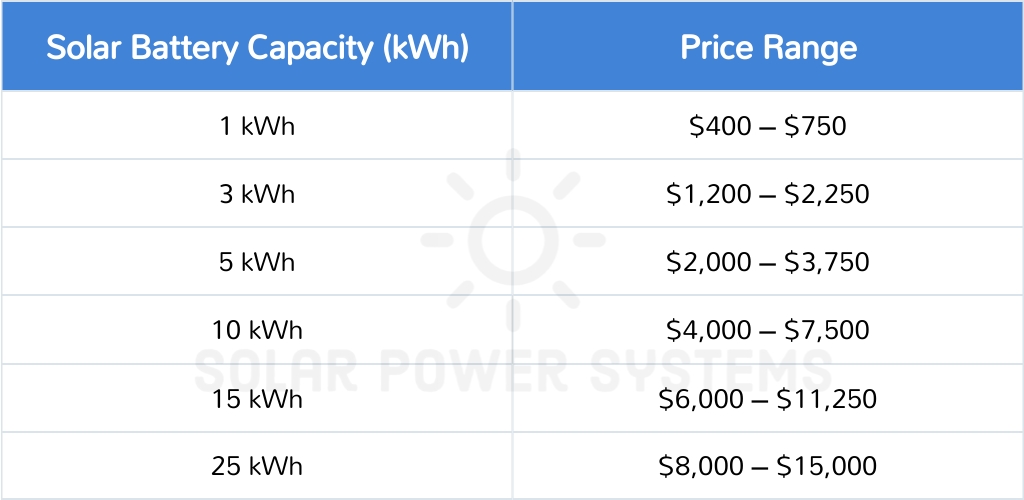
Furthermore, with the advancement of technology, battery backup systems are becoming more cost-effective. Prices are decreasing as a result of the increasing demand for reserve power supplies and developments in battery technology. Hence, although the initial investment may appear substantial, it is critical to contemplate the enduring cost reductions and advantages.
The Price of Backup Generators
Backup generators have been the preferred option for supplying domestic emergency power. By size, model, and manufacturer, the mean cost of a generator can vary substantially. The cost of a generator for home backup power can range from $4,000 to $25,000. As the cost of a generator will fluctuate based on its capacity, it is critical to assess and comprehend the power requirements of your residence.

Although generators may initially have a lower cost than backup battery systems, they incur ongoing expenses. Fuel, maintenance, and potential repair expenses are included. Fuel-powered generators, such as those powered by natural gas, diesel, or propane, can accumulate in price over time, particularly in the event of protracted blackouts.
It is critical to consider both the initial purchase price and the continuous operating and maintenance expenses when comparing the cost of batteries versus generators for residential power backup. Each alternative possesses advantages and disadvantages, and the optimal selection will be contingent upon your particular requirements, financial constraints, and personal inclinations.
Advantages of Backup Battery Over Generators
Advantages of Backup Batteries
Backup batteries for your home with a host of benefits that ensure uninterrupted power supply:
- The ability to ensure a smooth power transition in the event of a power disruption is the primary benefit of a battery backup system. Backup batteries are an ecologically sustainable alternative to generators due to their discreet operation, absence of emissions, and minimal maintenance needs.
- An environmentally sustainable solution for backup electricity can be achieved through the combination of a backup battery and a solar panel system. Peak electricity demand can be mitigated by utilizing the batteries’ conserved energy, which may result in reduced electricity costs.

Source: SGE Solar
- The average residential utility consumer in the United States consumes around 889 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy per month, as reported by the Energy Information Administration. A battery backup system may supply power for several hours to several days, contingent upon the battery’s dimensions and capacity.
- Battery backup systems may entail a substantial initial investment. However, future price reductions are anticipated due to technological advancements. According to a BloombergNEF report, battery energy storage costs $152 per kWh in 2023.
Advantages of Generators
Become acquainted with the variety of advantages that come with owning a backup generator for your residence:
- One of the generator’s benefits is that they supply electricity for an extended period of time, which renders them a dependable option in the event of protracted blackouts.

Source: Cashman Equipment
- Petrol, diesel, or natural gas are the typical fuels used to operate generators. They have the capacity to supply a substantial quantity of energy, which is sufficient to utilize critical domestic appliances and systems.
- A portable generator can power a few appliances for a small amount of time, while a stationary generator can power an entire home for 3,000 hours.
Conclusion
To sum up, a backup battery and a backup generator are both practical choices for residential power backup systems, and each has advantages of its own. For brief power outages, a backup battery—especially a solar battery—offers a quiet, environmentally responsible option, and as technology develops, battery prices should decline.
Albeit being louder and less ecologically friendly, generators provide a dependable alternative for prolonged power outages and can power a wider variety of equipment. The decision between a generator and a battery for home power backup should ultimately be made with the user’s energy demands, financial situation, and environmental factors in mind.


