Despite the well-known fact that water and electricity are incompatible, “green energy” advocates have their own interpretation of this statement. “Green” energy companies are increasingly turning their attention to bodies of water for installing floating solar panels.
In this blog post, we’re set to explore the vast potential of solar power atop water surfaces. Learn about the perks of floating solar systems, their installation journey, and how they’re making waves in benefiting the environment.
As you dive into the world of floating solar farms, remember that SolarPowerSystems is here to help you navigate your own path to renewable energy. If you’re inspired by what you read and want to explore how solar can work for you, don’t hesitate to visit our blog or get a personalized solar quote from our industry experts.
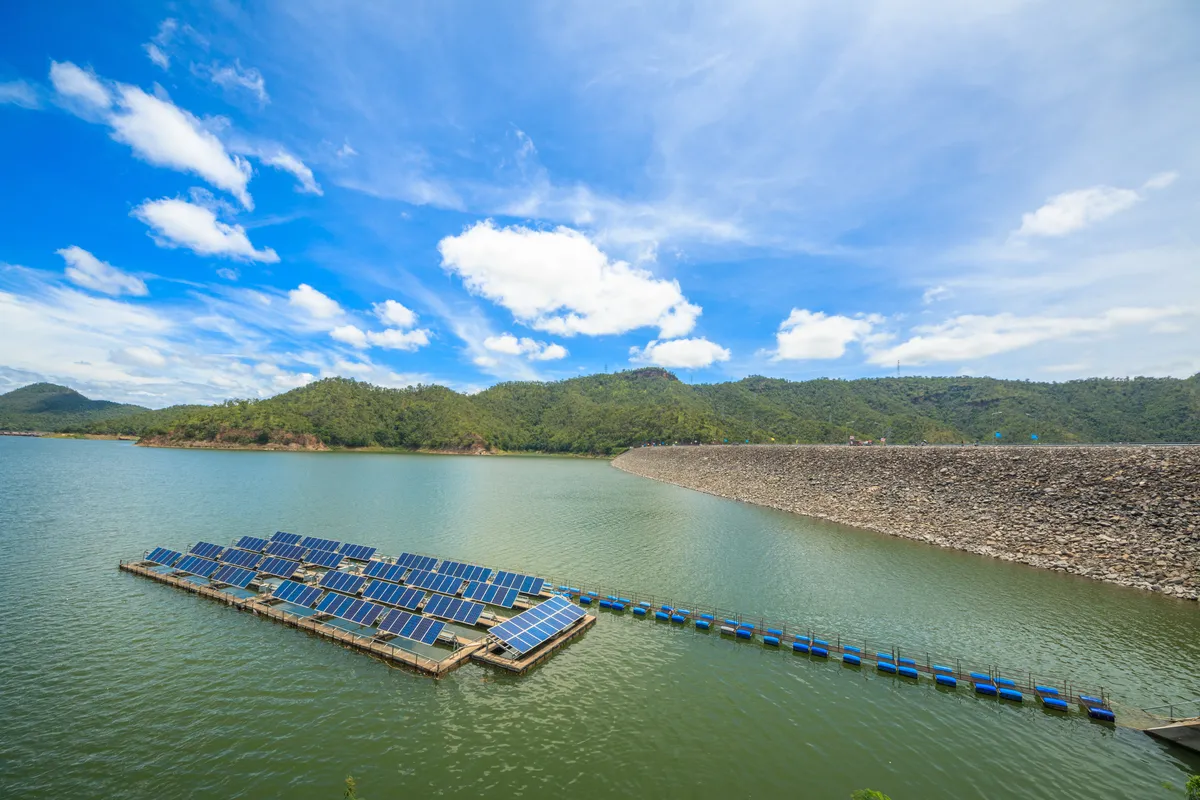

What Is Floating Solar?
Floating solar, also known as solar-on-the-sea or buoyant PV systems, refers to solar panels placed on top of a body of water. These panels are securely attached to floating structures, allowing them to ride the waves. You can find these floating solar panels on serene lakes and tranquil dams rather than rough seas.
Floating solar provides a green and completely clean way to produce electricity, combining marine and renewable energy technologies. In such a solar project, the power generated from these floating solar arrays is sent through underwater cables to a designated power hub.

How much is your electricity bill per month?
Help us understand what you`re currently spending
Brief History Behind Floating Solar Panels
South Korea was one of the pioneers in testing the waters with floating solar power systems. The government-owned Korea Water Resources Corporation (K-water) dipped its toes into the concept back in 2009, starting with a small 2.4-kilowatt (kW) model on the Juam Dam reservoir in Suncheon, South Jeolla Province.
By October 2012, they dove in deeper, setting up a hefty 500-kW commercial plant at the Hapcheon Dam in South Gyeongsang Province, following up on a successful 100-kW trial run at the same dam the year before. This marked the world’s first big-scale floating solar PV setup on a dam reservoir and South Korea’s inaugural floating solar farm.
Currently, the country is riding the wave with three operational commercial floating solar power facilities, aiming to contribute to the renewable energy tide up to 20% of the energy mix by 2030, from the current splash of 7%.
The Global Rise of Floating Photovoltaics
South Korea is in the process of constructing a colossal floating solar power plant set to become the largest globally. Situated on the Saemangeum tidal flats along South Korea’s western coastline, this project is projected to generate 2.1 gigawatts of electricity — ample to energize 1 million households, as per reports from the energy industry news site Power Technology.
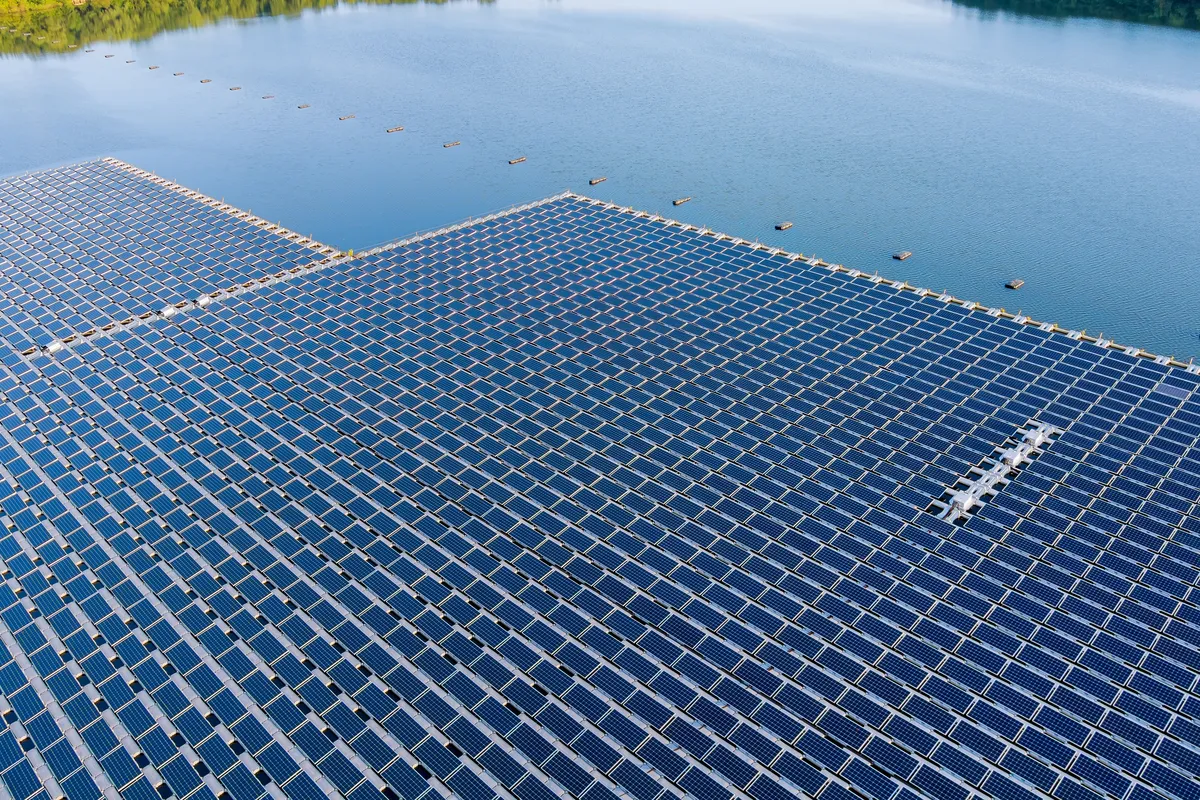

Meanwhile, Portugal boasts Europe’s largest floating solar farm. Resting atop the Alqueva reservoir, the continent’s biggest artificial lake, it caters to approximately one-third of the energy demand of neighboring towns. With 12,000 floating solar panels spread across an area equivalent to four football pitches, this floating solar farm stands as an impressive endeavor.
What Are the Key Components of a Floating Solar Project?
A floating solar power plant comprises the solar module, buoyancy body, and anti-corrosion material, which consists of both vertical and horizontal frames, inspection footrest, and module mount assembly.
| Solar panels | At the heart of floating solar farms lie PV panels, housing numerous solar cells that work their magic, turning sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect. |
| Floatation platforms | Floating PV panels are supported by floating platforms crafted from buoyant materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or other suitable substances, ensuring the panels stay afloat atop the water’s surface. |
| Converter | The DC electricity generated by the floating solar panels must be converted into alternating current (AC) for further use in electrical systems. This crucial conversion, optimizing electricity output for grid integration, is carried out by inverters. |
| Anchors | To keep the floating platforms firmly in place and prevent drifting caused by wind or currents, an anchoring system is needed. The latter ensures stability and precise positioning of the floating solar arrays on the water body. |
| Electrical infrastructure | After conversion, the AC electricity from the inverters travels through electrical cables to a substation or distribution point, ready for integration into the electrical grid for wider distribution or earmarked for local consumption. |
Source: ResearchGate
The solar module needs to be as resistant as possible against moisture, free of lead, dust-resistant, and capable of withstanding occasional splashes of water. It also needs to pass the drinking water test. The buoyancy body is crafted from polyethylene, which is built to handle 2.5 times its weight. Besides, K-water’s floating solar panels utilize Magnesium Alloy Coating Product, an alloy steel developed in collaboration with steel manufacturer POSCO, known for its high resistance to corrosion.
Advantages of a Floating Solar System
A floating solar system offers a range of benefits that redefine the landscape of renewable energy solutions.
| Making the most out of space | Floating solar panels show how to make the best use of available space, especially in areas where land is in short supply or too expensive. By setting up floating solar panels on water bodies like reservoirs, dams, and lakes, we avoid the need to take over valuable agricultural land or disturb natural landscapes. This clever approach lets us generate solar float energy without competing with other land uses. Moreover, it promotes harmony in our use of the land |
| Durability and security of solar project | Floating solar arrays are built tough for security and durability. “Sitting” on water makes them harder to reach, lowering the risk of damage or theft. Additionally, being out on the water means less wear and tear compared to land-based setups, so they last longer and need less upkeep. |
| Budget-friendly floating project | Floating solar panels can be easier on the wallet than land-based ones. You skip the hefty costs of buying land and prepping sites. Plus, being close to existing electrical infrastructure can mean big savings on integration and transmission costs. |
| Great energy efficiency | The combo of water and solar panels in floating PV systems gives a cooling boost that amps up solar efficiency. Water naturally cools the floating solar panels, keeping them from overheating like those on land. This cool-down can crank up panel efficiency by up to 15%, giving us more energy bang for our solar investment. |
| Reflecting the power of water | Water bodies have a knack for reflecting sunlight, which works wonders for floating solar panels. The sunlight bouncing off the water and onto the panels means more photons get converted into electricity. This ‘mutual’ effort pumps up the energy output, making floating solar systems a top choice for squeezing the most out of solar power. |
| Algae control | Those floating solar panels aren’t just good for energy — they’re also great for keeping algae in line. Algal blooms, fueled by too much sun and nutrients, can wreak havoc on water quality and ecosystems. But by shading the water, floating solar panels can help keep algae growth under control, keeping the aquatic environment healthy. |
| Fish-friendly setup | Early studies suggest that floating solar panels have a lighter touch on aquatic life compared to other water-based structures. By carefully designing and placing them, we can minimize disruption to aquatic habitats, letting floating PV panels “coexist” peacefully with the underwater world. |
| Water conservation | Floating solar panels pull double duty by saving water, too. By shading the water underneath, they help cut down on evaporation, which is crucial in dry areas where water’s in short supply. Plus, by blocking out sunlight, they can help keep algae growth in check, which means cleaner water for all. |
Where Is the Best Place for Floating Solar Power Farms?
Despite the fact that most oceanic regions encounter storms, certain Equatorial areas remain tranquil and calm. Hence, relatively cost-effective engineering structures could be adequate to shield offshore floating solar panels. Immense fleets of floating solar panels on serene waters near the Equator have the potential to offer boundless solar power to densely populated nations in Southeast Asia and West Africa.
According to the latest study, just the offshore solar project in Indonesia could churn out approximately 35,000 terawatt-hours (TWh) of solar energy annually, akin to the current worldwide electricity output (30,000TWh per year).
However, nations with bustling populations like Nigeria and Indonesia will find themselves squeezed for room when it comes to harvesting solar energy inland. Being situated in the tropical doldrums, they also face a shortage of wind resources. Thankfully, these countries, along with their neighboring counterparts, can tap into boundless energy reserves by deploying floating photovoltaics atop tranquil equatorial waters.
Moreover, floating solar panels can be positioned on inland lakes and reservoirs, so the potential for inland floating solar is huge.
Areas that do not experience waves exceeding 6 meters in height or winds surpassing 15 meters per second hold the potential to produce up to 1 million TWh per year. This amounts to roughly five times the yearly energy requirement for a fully decarbonized global economy that sustains 10 billion prosperous individuals.
The prime locations predominantly lie near the Equator, particularly in and around Indonesia and equatorial West Africa. These regions witness rapid population expansion and possess high environmental values. Employing marine floating power plants could aid in mitigating conflicts over land use.
How Do Floating Solar Farms Work?
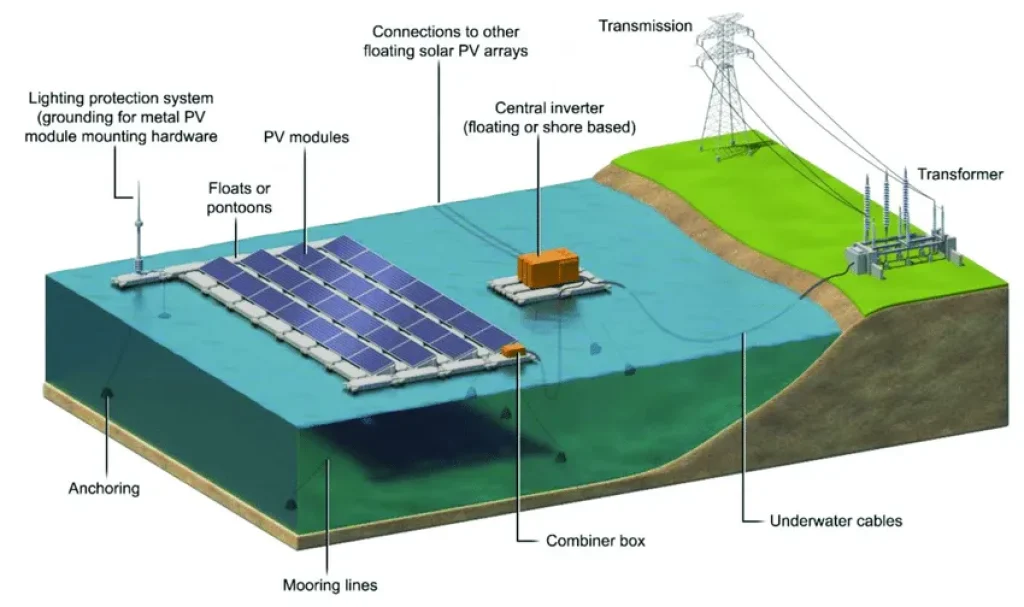
Floatovoltaics, also known as floating solar, is a solar power setup on a solid platform, that is placed on water bodies. In contrast to traditional solar PV plants, floating PV employs pontoons (which can bear heavy loads) as floats. Besides, the gear for floating solar panels includes power converters, anchoring systems, cables, PV modules, transformers, etc., for operation.
The pontoons support the PV modules on their surface, held in place by the anchoring system with mooring lines to ensure stability. A combiner sits alongside the modules, merging transmissions from multiple modules on the pontoon. These transmissions are then sent to a central inverter, floating on a separate pontoon, which connects to other arrays in the plant. It’s then linked to a transformer, ultimately transmitting electricity.
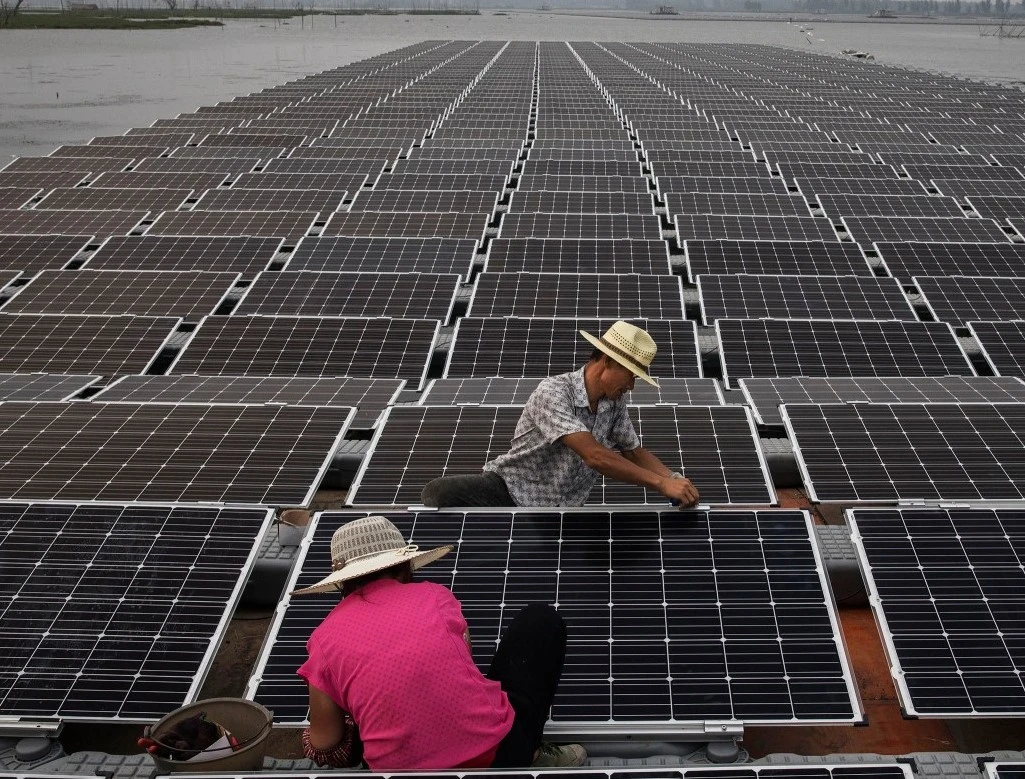

Source: Time
Floating and Land-Based Systems: Comparing Legal and Financial Aspects
| Floating PV | Land-based PV | |
| Investment |
|
|
| Regulation and permits |
|
|
| Experience |
|
|

Installation of Floating Power Plant
Setting up floating solar panels is a miscellaneous project: it demands meticulous planning and flawless execution for a smooth and effective installation. Below are the key stages in the installation journey:
- Site selection
- Assessment of the environmental impact
- Design and materials of the floating solar panels
- Anchoring and mooring systems
- Maintenance and cleaning
- Integration with hydropower plants
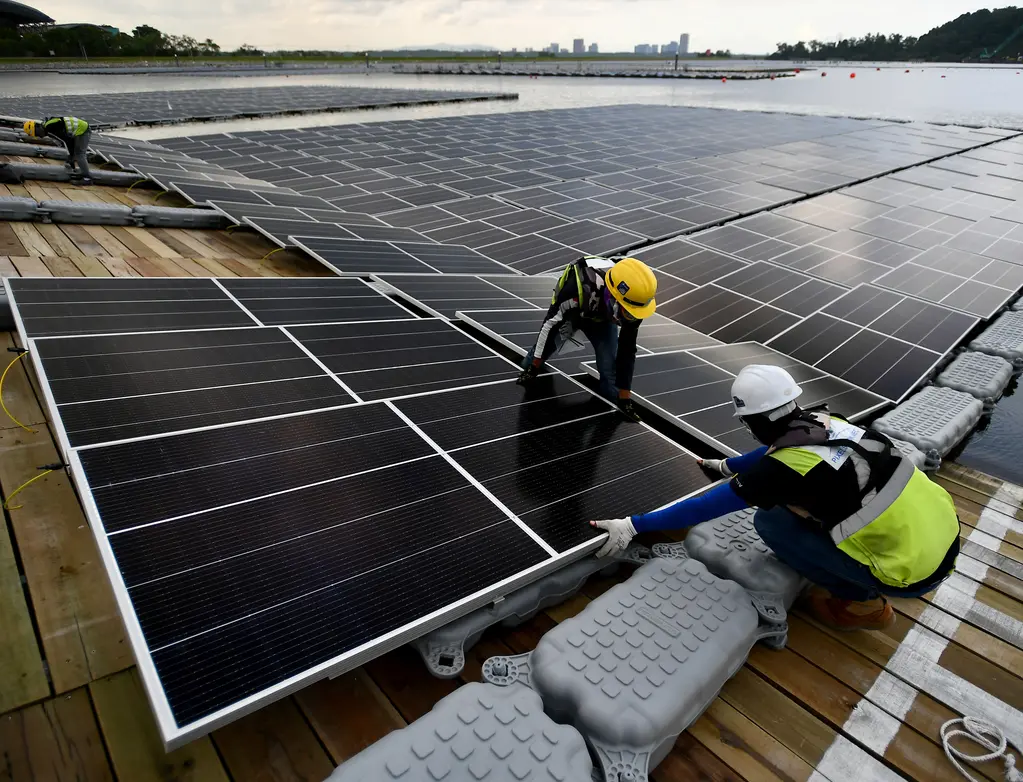

Source: World News Day
Let’s take a look at each aspect closely to see what it implies.
- Site selection: Choosing the perfect spot for a mobile solar project is a bit like searching for hidden treasure – you’ve got to factor in things like water depth, cleanliness, wind patterns, and sunshine levels. Being close to the grid link and demand hubs ensures minimal energy loss and maximum delivery efficiency.
- Environmental impact assessment: Before launching a mobile solar project, specialists need to carry out a thorough Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). It’s comparable to surveying uncharted territory before settling in. Correctly identifying potential ecological risks enables effective mitigation, safeguarding marine habitats, while a thorough assessment of potential impacts ensures the preservation of water quality and minimizes disturbance to aquatic flora.
- Design and materials of floating aolar panels: If you set to choose the right float design and materials, it feels akin to crafting a sturdy ship for an epic voyage. Opt for top-quality and long-lasting materials that can weather the unforgiving water environment, including UV rays, saltwater corrosion, and other potential impacts. Safety measures should be paramount in design, installation, maintenance, and hassle-free expansion.
- Anchoring and mooring systems: Similarly, keeping the floating solar arrays anchored securely seems as if you tether a mighty ship in stormy seas. Undoubtedly, an effective mooring system tailored to local water movements and wave actions ensures stability. Furthermore, proper grounding not only safeguards the floating solar panels from damage but also protects aquatic life.
- Floating solar upkeep and cleaning: Despite floating solar panels being a massive and solid structure, they require careful tending to ensure optimal performance. Therefore, PV panels specialists implement a well-developed maintenance plan, which includes routine checks, cleaning schedules, and repair protocols. Besides, to enhance system efficiency and streamline floating solar upkeep, people use automated cleaning systems or some other robotic solutions.
- Unification with inland hydropower plants: Integrating mobile floating solar panels with existing hydropower plants is like blending two powerful forces for greater impact. If PV specialists harmonize their operations, energy production becomes streamlined, and load balancing improves. In their turn, hydropower plant reservoirs provide ideal settings for a floating solar system and maximize its potential.
Disadvantages of Floating Solar Panels
| Higher cost of maintenance | Keeping solar panels afloat on water surfaces presents additional hurdles and increased expenses, demanding specialized gear and expert personnel. It’s absolutely crucial to stay on top of regular cleaning to maintain the most efficient panel performance. |
| Adverse effects of water | Solar panels are designed to be waterproof to endure rainfall, but constant exposure to water around the clock could potentially harm them. If any panels were to break, they’d be even more vulnerable to water damage. However, this potential drawback shouldn’t deter the installation of floating solar panels. |
| Limited usage | This technology doesn’t fit all shapes and sizes. Plenty of floating solar panels are geared towards big fish like large corporations or utility companies. For folks or outfits looking for solar power, going for rooftop or ground-mounted solar setups is a more down-to-earth choice. |
Geography Of Floating Solar Farms
Most floating solar power plants pile up in the equatorial regions of Asia and Africa. For instance, Indonesia has vast solar power potential, and in 2023, they created the largest floating solar power plant in the world.
Many other big floating solar projects are realized in China, Japan, Thailand, etc. However, Europe is following suit and looking for suitable locations to harness solar power in the same way.
As the world embraces this innovative approach to renewable energy, there’s no better time for you to join the movement. Visit SolarPowerSystems to learn more about how you can benefit from solar energy and get a personalized solar quote today. Let’s work together to power a greener future!
Navigating the Horizon with Floating Solar Panels
The offshore floating solar sector is still in its early days. While these panels offer many advantages, they have some drawbacks compared to land-based panels, such as susceptibility to salt corrosion and marine fouling. It’s preferable to anchor floating solar panels in shallow seas, but great care must be taken to minimize harm to marine life and fishing activities. Furthermore, the shifting wind and wave patterns due to global warming could pose additional challenges.
Nevertheless, we anticipate that offshore floating solar panels will play a significant role in the energy mix for nations with access to tranquil equatorial waters. In a groundbreaking shift, by the mid-century, approximately a billion people in these regions are anticipated to depend heavily on solar energy, marking the most rapid transformation in the history of energy.


