Inverters are essential components within the vast domain of power electronics. Critical components are employed in the transformation of direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), a procedure that is indispensable for the functioning of numerous household appliances and devices. Pure sine wave (PSW) inverters and modified sine wave (MSW) inverters are two notable categories within the wide-ranging spectrum of inverters. From 2022 to 2027, the global inverter market is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7% from a value of $16.3 billion in 2022.
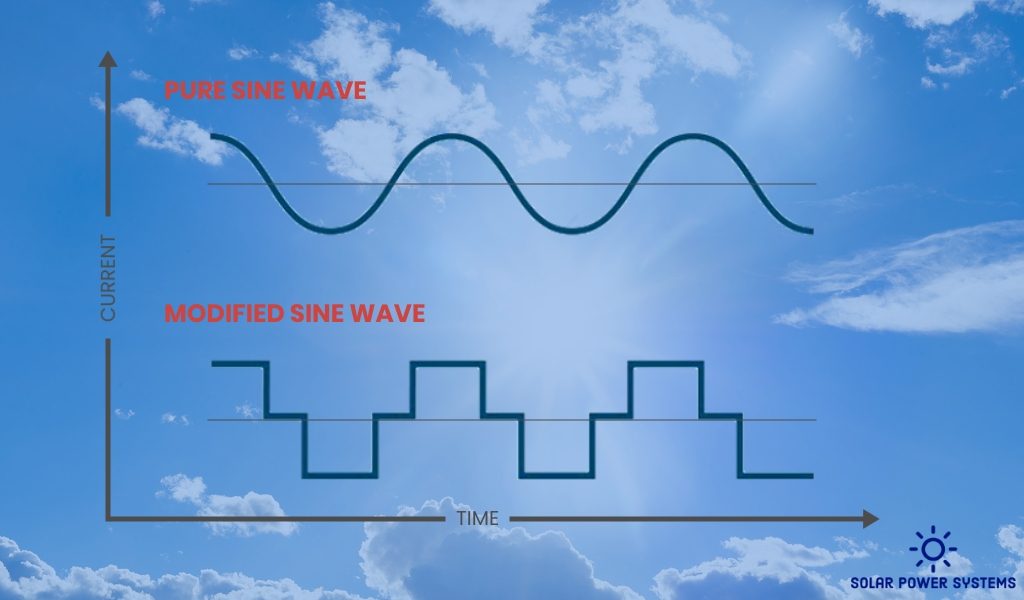
Inverters that generate pure sine waves, as their nomenclature implies, simulate the conventional power infrastructure by generating a continuous, uninterrupted wave. These inverters are renowned for their exceptional performance and low electrical noise output.

Conversely, a substantial segment of the inverter market is comprised of modified sine wave inverters, which produce a waveform resembling steps. These inverters are popular with consumers due to their low cost and simplified design.
Nevertheless, there are some complexities involved in deciding between a modified sine wave and pure sine wave inverters. Understanding the precise attributes and usage context of these terms is of the utmost importance. When one takes into account the efficiency of energy conversion, the compatibility with a variety of appliances, and the uniformity of the output wave, this comprehension becomes especially vital.
What Is the Solar Inverter?
A solar energy system must include a solar inverter as a fundamental component. This device converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into the more usable alternating current (AC) for the purposes of powering the residence or place of business. For a complete understanding, you need to familiarize yourself with the basic facts about solar inverters:
- Transformation mechanism: DC energy is produced by solar panels. However, the majority of home appliances operate on AC power. Solar panels produce functional energy; therefore, they would be useless without a solar inverter.
- Different types: in solar energy systems, inverters can be classified into two main categories: modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters.
- Efficiency: inverters employing pure sine wave technology exhibit superior efficiency compared to those utilizing modified sine wave. By generating a continuous, steady wave, they enhance the output’s stability and dependability. Ensuring this pertains to the power supply for delicate electronic devices.
- Durability: extended longevity and reduced failure rates are characteristics of pure sine inverters in comparison to modified sine wave inverters, as indicated.
How Inverters Work and Why They Are Needed When Installing Solar Panels
Without exception, inverters are vital components of any solar power system. The energy harvested by your solar panels would be rendered useless in the absence of an inverter. The operation of a solar inverter consists of the following stages:
- The sun shines on solar panels, designed with semiconductor layers of crystalline silicon. Solar panels are responsible for transforming incident sunlight into direct current (DC) electrical energy, which is then delivered to the inverter.
- The inverter receives a direct current of energy and passes it through a transformer, resulting in an alternating current (AC) output.
- Excess power can either be sent back into the grid or to a battery storage system. That depends on the solar system you have chosen for the property.
Consequently, why is an inverter necessary for a solar installation? The solution can be found within the characteristics of our electrical grid and the appliances that we employ. AC power is utilized by the overwhelming majority of electrical appliances and systems found in residences and businesses. Although DC power can be advantageous for specific tasks like charging batteries, it is not optimal for operating the majority of residential appliances.
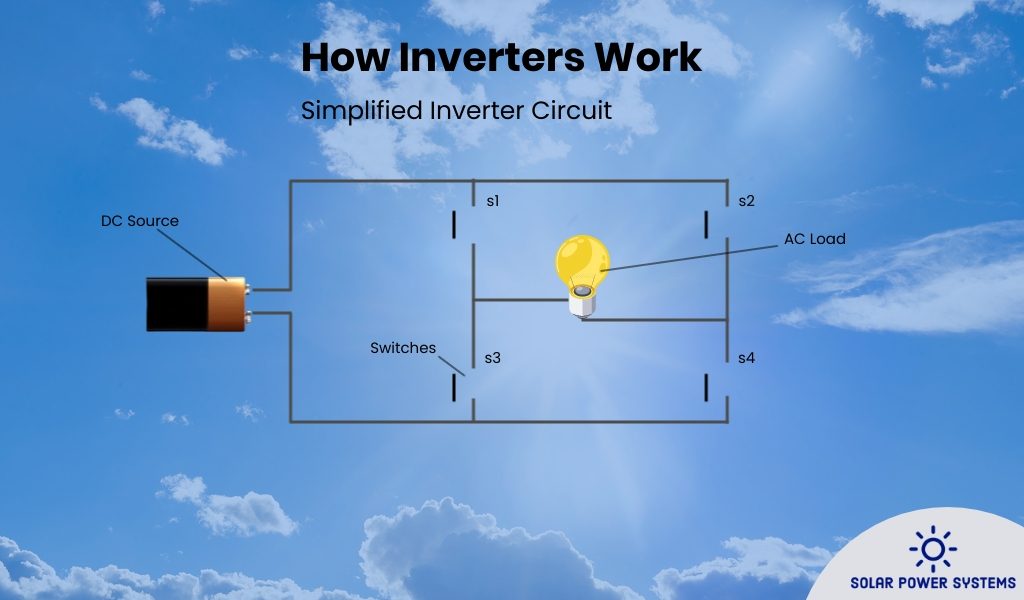
The issue, however, is not compatibility alone. Additionally, inverters guarantee the efficiency and security of your solar energy system. By regulating the voltage and current supplied by the solar panels, they effectively mitigate the risk of damage that may result from power fluctuations. In addition, contemporary inverters are outfitted with sophisticated functionalities such as remote monitoring and fault detection, which facilitate the processes of upkeep and resolution of issues.
What Is a Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
The voltage output of pure sine wave inverters consists of sine waves. Many utilities deliver sine wave output. Because of this, grid-connected systems must always utilize pure sine wave inverters. Generally, pure sine wave inverters are required for sensitive equipment, including new televisions, microwaves, and refrigerators. The following are the main aspects of a pure sine wave converter:
- Conversion process: the conversion process of the pure sine wave inverter is distinctive in that it generates an electrical waveform that is seamless, uninterrupted, and precise to that of the conventional electrical grid. This indicates that the polarity of the output voltage changes instantaneously when it descends below zero and rises and falls in a steady fashion. Thus, a more efficient and hygienic power output is produced.
- Complex circuitry: inverters working exclusively with pure sine waves are constructed with circuitry that is more intricate in nature compared to those that utilize modified sine waves. This intricacy contributes to the generation of a sine wave output that is uniform and seamless.
- Compatibility: pure sine wave inverters are compatible with the vast majority of AC electrical devices on account of their seamless sine wave output. Sensitive electronics that require a consistent and hygienic power supply are thus ideally suited to be powered by these devices.
- Security: pure sine inverters are generally safer to operate because they prevent electronic devices from overloading and prolong their lifespan.

What Is a Modified Sine Wave Inverter?
When modified sine wave inverters are utilized, the polarity changes abruptly from positive to negative. When observing the wave, one discerns a square, stair-step pattern in which the polarity alternates. This surge may cause damage to more fragile, sensitive apparatus. Key points to consider when choosing a modified wave inverter:
- Operational mechanism: the modified sine wave inverter functions by generating an alternating current voltage waveform that, to a certain degree, emulates the sine wave configuration observed in electricity in residential. However, this inverter produces an approximated, incremental sine wave as opposed to a pure, seamless sine wave.
- Power generation: for the modified wave converter to make an alternative current, it needs three voltage levels: positive, zero, and negative. The scheme looks like a circle sine wave because it goes back and forth between these three voltage levels. Compared to a sine wave converter, this is easier to make and costs less.
- Compatibility: the majority of appliances are compatible with modified sine wave inverters. Due to the irregular waveform, however, specific sensitive electronic components may not offer optimal performance.
- Efficiency: the inverters operating on modified sine waves are generally less energy-efficient. A modified sine wave inverter may achieve an efficiency ranging from 75% to 85%.
- Electrical noise: an attribute of modified sine wave inverters is their potential to generate increased levels of electrical noise. Occasionally, this may result in interference with particular electronic devices.

Source: Elinz
Pure Sine Wave vs Modified Sine Wave
Pure sine wave versus modified sine wave inverters is frequently the subject of debate regarding power inverters. You can make a more informed choice if you comprehend the benefits of both options.
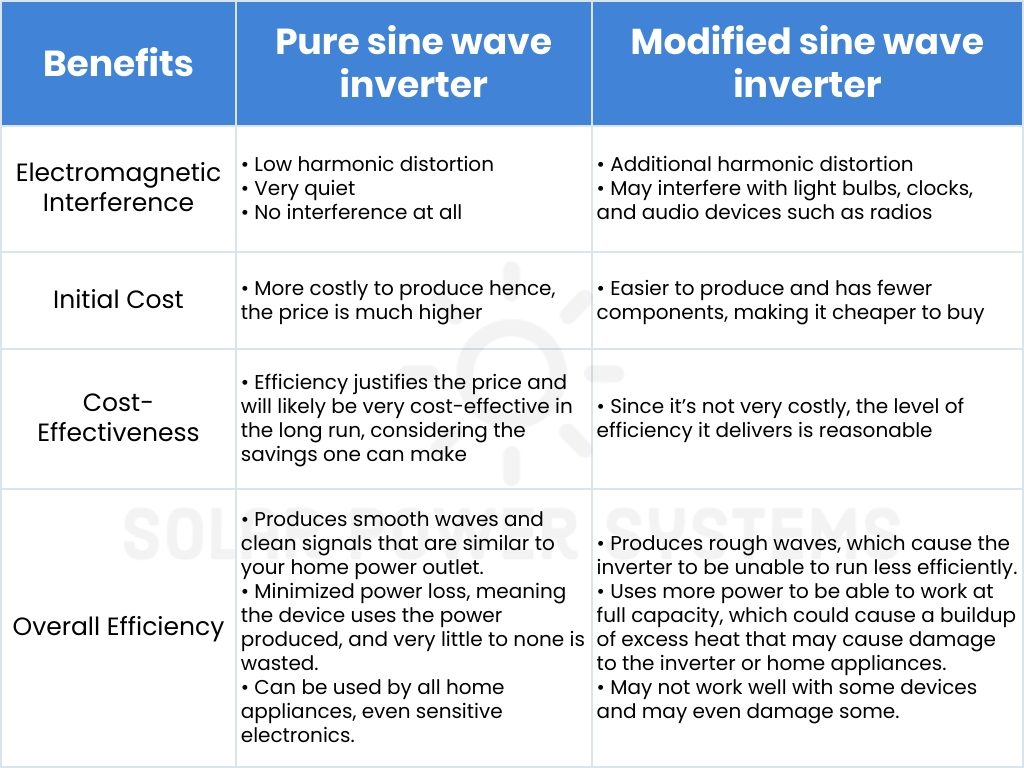
- Efficiency: inverters utilizing PSW exhibit greater efficiency in comparison to those utilizing MSW. They reduce energy loss by converting power without producing an inordinate amount of heat. Energy savings of up to 20% are possible due to this efficacy.
- Compatibility: particularly sensitive electronics are not an issue for PSW inverters, as they are compatible with virtually all equipment types. Medical equipment, microwaves, and laser printers are examples of devices that may experience operational complications when using MSW inverters despite their lower cost.
- Performance: in contrast to devices powered by MSW inverters, devices powered by PSW inverters generally operate more effortlessly and silently. Similar to the power supplied by utility companies, PSW inverters generate a consistent, steady wave.
- Longevity of devices: connected devices are less prone to damage by continuously operating PSW inverters. The life of sensitive electronics can be significantly reduced as a result of the inaccurate and blocky wave generated by MSW inverters.
MSW inverters have advantages compared to PSW inverters. For systems in which the burden does not necessitate a pure sine wave, MSW inverters are favored due to their reduced cost. An MSW inverter can also operate similarly to a PSW inverter for tiny appliances and non-sensitive equipment.
How Large Must an Inverter Be to Power a House
If you use a pure sine wave converter, you may be able to save power. However, the exact size you need will depend on how much power your whole house uses, which you can find by adding up the wattages of all your devices. Let’s take a look at what size and power inverters come in:
- Pure sine wave inverter size: a pure sine wave inverter should have a capacity of about 3000 to 6000 watts so that it can power all the items in a home. This size is good for handling the total energy needs of your fridge, air conditioner, lights, and other important equipment. To start up, some motorized products like freezers and air conditioners need a rush of power, which is what pure sine wave converters can handle.

Source: LuxpowerTek
- Modified sine wave inverter size: a modified sine wave inverter would have to be much bigger so it could power all of your home’s utilities. Modified sine wave inverters aren’t as good at turning DC power into AC power. The energy needs go up because appliances that use these transformers tend to use more power.
Cost of the Two Main Types of Inverters
Regarding inverter costs, pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are noticeably different in price.
- Pure sine wave inverters: owing to their sophisticated technology, which provides superior efficiency and compatibility with electronics, these inverters are usually more costly. The typical price range for a pure sine wave inverter is between $100 and $500. Power capacity and extras like digital screens, integrated USB ports, and remote control functionality affect the price.
- Modified sine wave inverters: this type is more reasonably priced, which makes them a well-liked option for customers on a tight budget. These inverters may cost anywhere from $200 and $300 for a 3000-watt power capacity. But beware—they may not function well with every electrical item, despite their cheaper price.
To Sum Up
Personal preferences and the electronic devices in operation are, in summary, determining factors in the selection between modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Although on the pricier side, pure sine wave inverters offer enhanced compatibility, durability, and efficiency for electronic devices, rendering them an optimal selection for such equipment. Conversely, modified sine wave inverters operate at a lower energy efficiency and may not be compatible with all devices.
Customers will be able to maximize the performance of their electronic devices and make well-informed decisions with the assistance of a thorough comprehension of both varieties of inverters. Recognizing the intricacies of these technologies will be essential for capitalizing on the anticipated substantial expansion of the worldwide inverter market. When an inverter, it is critical to take into account the immediate as well as long-term expenses and advantages.


